System Dynamics Helps Farmers Escape Poverty Trap in Guatemala
EXECUTIVE Summary
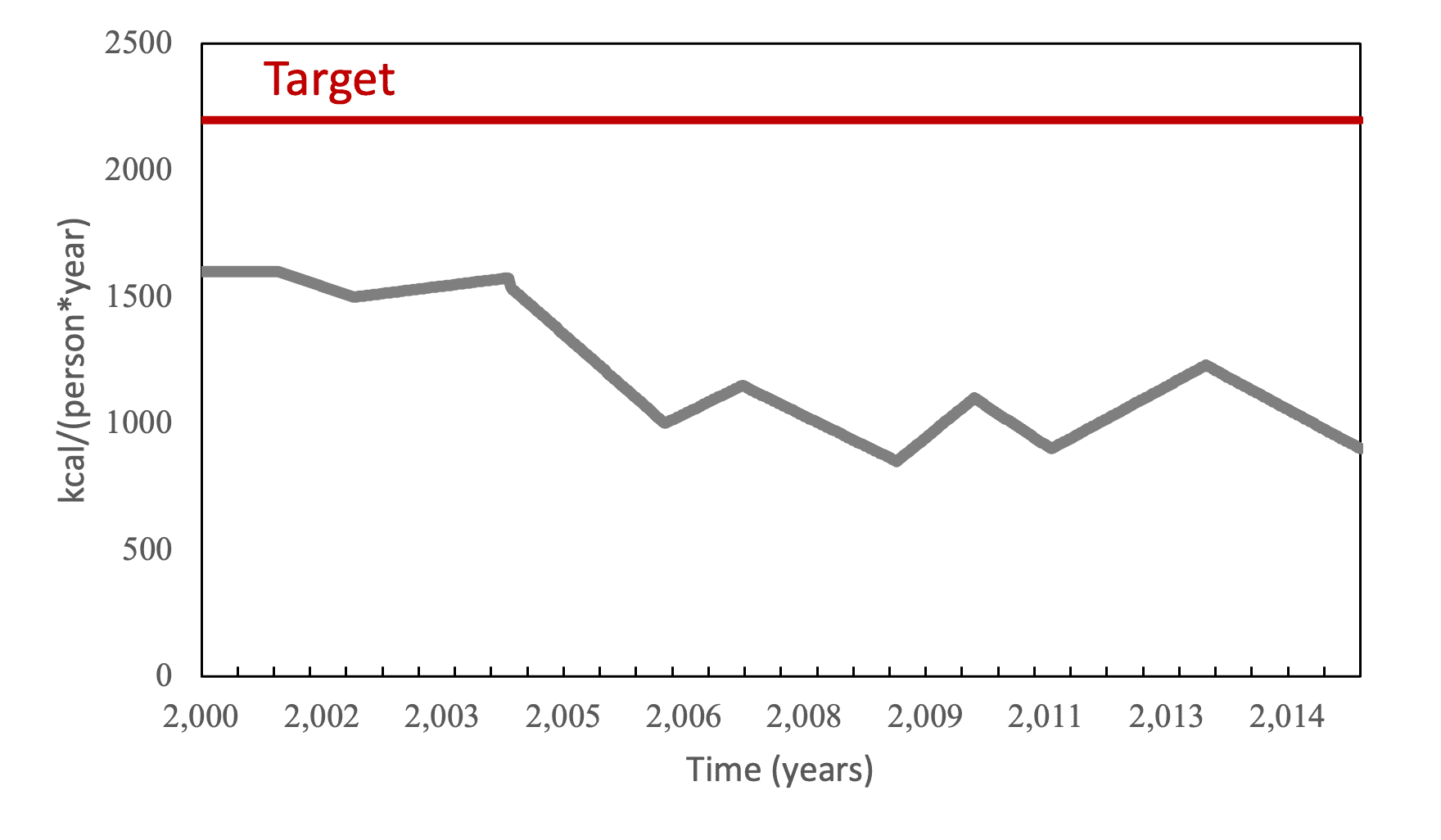
Guatemala holds the 4th highest global ranking for chronic malnutrition, and climate change is intensifying the challenges subsistence farmers face in providing food for their families. Utilizing a System Dynamics model facilitated meaningful discussions among various stakeholders and government entities, ultimately leading to the provision of strategic resources, such as livestock and expert guidance, for 152 families. This support enabled farmers to break free from the poverty trap and make valuable investments in their agricultural endeavors.
The System Dynamics model effectively illustrated the interplay between numerous variables, empowering farmers to comprehend and take control of key leverage points essential for their well-being and prosperity.
#Food security #Farmers #Agriculture #Guatemala
The Problem
Guatemala faces a staggering 55% prevalence of chronic malnutrition (a widely recognized indicator of food insecurity) in rural areas and ranks as 4th worst globally. Climate change is amplifying the difficulties subsistence farmers in Guatemala face in providing food for their families. Although climate change affects all food producers in various ways, subsistence farmers are especially vulnerable due to their limited access to irrigation and crop insurance, which could help mitigate the effects of fluctuating weather conditions. Furthermore, because subsistence farmers depend on their own production to feed themselves and their families, low yields and crop loss often result in malnutrition and starvation.
This underscores the need to understand how local farmers can collaborate and work with both local and central governments to enhance their food security.
The Solution
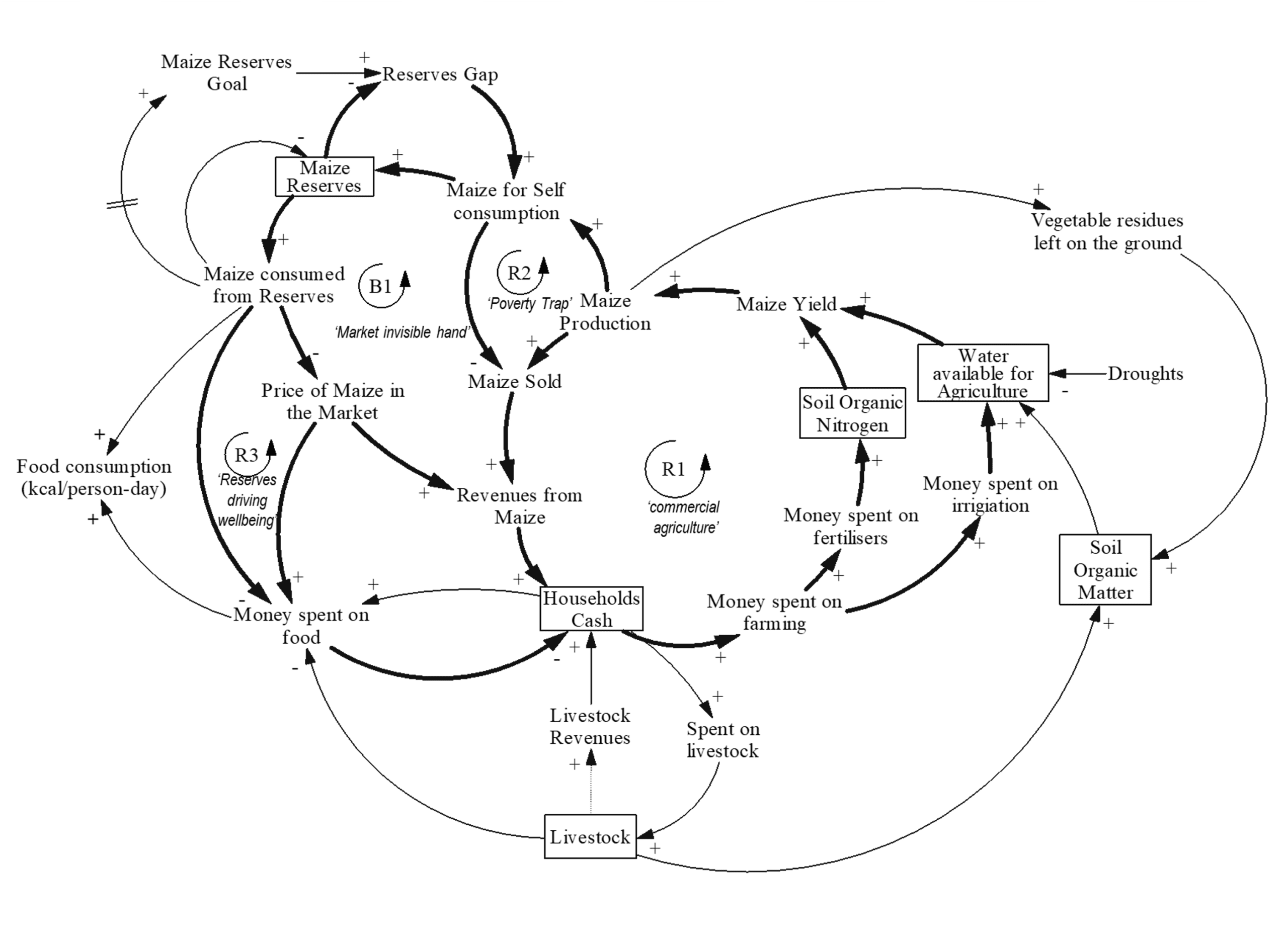
The model was developed using Group Model Building (GMB) and stakeholder engagement in two distinct communities. In each case, we collaborated with farmers and representatives from central and local governments to create causal loop diagrams that illustrated the primary relationships within their respective food systems and the variables influencing food security resilience in the face of climate change. This understanding was then converted into quantitative System Dynamics (SD) models, which facilitated discussions regarding potential policies.
The model comprises five main components:
-
Maize local market: This component captures the primary dynamics of the local market using a traditional commodity model.
-
Households: This element represents the dynamics affecting household cash availability and purchasing power, with revenues generated from maize production, livestock, and other activities.
-
Livestock: This component illustrates the primary dynamics of livestock (specifically poultry) production on local farms.
-
Soil: This part demonstrates the dynamics of organic nitrogen and organic carbon in the soil.
-
Water and irrigation: This component captures the infrastructure used for irrigation and exogenous variables like rainfall.
The model features three main feedback loops:
-
Commercial agriculture (R1): Revenue from maize increases household cash, which enhances their ability to invest in farming (such as seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation systems), resulting in improved soil quality and increased water uptake.
-
Poverty trap (R2): A portion of maize production is allocated for self-consumption. The higher the proportion dedicated to self-consumption, the less maize is available for the market, which reduces revenue and subsequently investment in farming. Low investment in farming leads to low yields, further decreasing the amount of maize that can be sold.
-
Reserves driving wellbeing (R3): Higher production rates result in more maize being available for self-consumption, reducing the need to spend money on purchasing food. This increases farmers’ available cash for investing in the next year’s harvest.
Outcomes
The policy recommendations from our study were utilized by local NGOs and government representatives to lobby their representatives in parliament and the Minister of Agriculture (MAGA). As suggested in the report, 152 families were provided with livestock in small quantities and supported by technical experts to develop small production farms.
This demonstrates the compelling nature of using System Dynamics in addressing complex issues, such as food security in the context of climate change. System Dynamics enabled to graphically represented the system through causal loop diagrams, providing a crucial visual aid that facilitated communication with local stakeholders in a way that other modeling approaches, mainly focused on mathematical formulations, could not achieve. Further, the emphasis on stocks in System Dynamics allowed for the effective representation of food stocks and key resources like soil organic matter, while maintaining model simplicity.
OTHER SUCCESSFUL APPLICATIONS
Solving Bottlenecks in Dairy Production Facilities with System Dynamics
Solving Bottlenecks in Dairy Production Facilities with System Dynamics EXECUTIVE Summary FrieslandCampina faced potential bottlenecks in production due to the merging of two factories. They hired SD&Co which employed system dynamics simulation models to predict...
A Design Value Calculator: A System Dynamics Boardgame
A Design Value Calculator: A System Dynamics Boardgame EXECUTIVE Summary Product design is a specific form of complex innovation that touches all areas of an organization’s management. While entrepreneurs recognise the value of design, they often tend to focus...
The World Bank Uses System Dynamics to Identify Root Causes of Poverty
The World Bank Uses System Dynamics to Identify Root Causes of Poverty EXECUTIVE Summary Madagascar has one of the highest poverty rates in the world. In 2022, an astonishingly three out of every four people in Madagascar lived below the poverty line. Poverty has...
Upcoming Events
Health Policy SIG Networking and Collaboration Event
Please join us for our quarterly Health Policy SIG virtual social hour! Agenda: TBD
Recent Posts
Society Governance Updates
Society Governance Updates Welcome, Allyson! New President Allyson Beall King joined the Policy Council as our 2024 President. Her primary role is as director of the Washington State University School of the Environment, which focuses on regional ecologies and our...
Call for Presenters: Seminar Series
Call for Presenters: Seminar Series We at the System Dynamics Society are continually seeking vibrant and knowledgeable presenters for our ongoing Seminar Series. As we unfold the calendar, there’s always a place for more insights, experiences, and expertise to enrich...
Honoring Excellence: A Glimpse into the Awards of the International System Dynamics Conference
Honoring Excellence: A Glimpse into the Awards of the International System Dynamics Conference The International System Dynamics Conference brings together experts, practitioners, and students to exchange ideas, showcase real-world applications, and celebrate...
Join us
OTHER SUCCESSFUL APPLICATIONS
Solving Bottlenecks in Dairy Production Facilities with System Dynamics
Solving Bottlenecks in Dairy Production Facilities with System Dynamics EXECUTIVE Summary FrieslandCampina faced potential bottlenecks in production due to the merging of two factories. They hired SD&Co which employed system dynamics simulation models to predict...
A Design Value Calculator: A System Dynamics Boardgame
A Design Value Calculator: A System Dynamics Boardgame EXECUTIVE Summary Product design is a specific form of complex innovation that touches all areas of an organization’s management. While entrepreneurs recognise the value of design, they often tend to focus...
The World Bank Uses System Dynamics to Identify Root Causes of Poverty
The World Bank Uses System Dynamics to Identify Root Causes of Poverty EXECUTIVE Summary Madagascar has one of the highest poverty rates in the world. In 2022, an astonishingly three out of every four people in Madagascar lived below the poverty line. Poverty has...
Recent Posts
Society Governance Updates
Society Governance Updates Welcome, Allyson! New President Allyson Beall King joined the Policy Council as our 2024 President. Her primary role is as director of the Washington State University School of the Environment, which focuses on regional ecologies and our...
Call for Presenters: Seminar Series
Call for Presenters: Seminar Series We at the System Dynamics Society are continually seeking vibrant and knowledgeable presenters for our ongoing Seminar Series. As we unfold the calendar, there’s always a place for more insights, experiences, and expertise to enrich...
Honoring Excellence: A Glimpse into the Awards of the International System Dynamics Conference
Honoring Excellence: A Glimpse into the Awards of the International System Dynamics Conference The International System Dynamics Conference brings together experts, practitioners, and students to exchange ideas, showcase real-world applications, and celebrate...
Upcoming Events
Health Policy SIG Networking and Collaboration Event
Please join us for our quarterly Health Policy SIG virtual social hour! Agenda: TBD



Based on the principle and definition of feedback loop, are R2 R3 and B1 feedbak loops? The arrows do not form cyclic connections.